In the past, users faced many traditional barriers in accessing satellite imagery, from complicated request processes, limited coverage to delayed image delivery times. These have had a significant impact on the use of satellite imagery to solve real-world problems.
Now, with the increasing demand for real data and the strong development of science and technology, artificial intelligence has brought new satellite tasking solutions, allowing users to proactively place images and explore space in their own way. In this article, we will help you understand how on-demand photography works, how to use available spatial data platforms, and how to optimize efficiency to maximize the power of data from space.
What is satellite tasking?
Satellite tasking is the process of requesting a satellite operator to collect new, high-resolution imagery of a specific Area of Interest (AOI) based on your specific needs. Unlike satellite imagery stored in a database, on-demand imagery is created from scratch for the purpose of monitoring change, responding to events, or conducting in-depth research.
While it may sound simple, accessing real-time satellite imagery isn’t always easy. Many users struggle to understand the potential costs, assess the feasibility of the mission, and have enough control over the process to maximize their investment. Satellite tasking delivers accuracy and timeliness, but to get the most out of it, you need to understand how it works.

The evolution of satellite tasking
The ability for commercial entities to request satellite imagery on demand represents a relatively recent advancement in the history of remote sensing technology. What was once tightly controlled by governments has gradually evolved into a more open system, enabling private sector participation and expanding civil applications.
- Pre-1990s: Satellite imagery was exclusively controlled by government and military organizations, primarily for national defense and intelligence purposes. Access to such data by the general public or private entities was virtually nonexistent.
- 1992: The Russian Federation marked a pivotal turning point by beginning to commercialize satellite imagery, allowing civilian and commercial customers to purchase data captured by its satellites.
- 1994: The United States officially authorized private companies to design, launch, and operate commercial Earth observation satellites, paving the way for rapid growth in the commercial satellite imaging industry.
- 1999: The launch of IKONOS-2, the first high-resolution commercial imaging satellite, marked a major milestone. For the first time, commercial users could access detailed satellite imagery suitable for a wide range of practical applications.
- 2010s: The emergence of web-based platforms began to streamline the satellite tasking process. Users no longer needed to navigate complex procedures or rely on time-consuming email correspondence with satellite providers.
- Today: Modern platforms such as GEOHUB have redefined the user experience, enabling intuitive, fast, and user-friendly online satellite tasking. Imagery can now be captured and delivered within days rather than the weeks or even months required in the past making the technology far more accessible and responsive to time-sensitive needs.
The challenges of satellite tasking
Despite its immense potential, satellite tasking continues to face several critical challenges that hinder broader accessibility and effective utilization of this technology.
Complex and fragmented processes
The lack of streamlined workflows and clear operational guidance presents a significant barrier to the expansion of satellite tasking services. The process is far from straightforward. The technological complexity, coupled with limited connectivity among users, providers, and stakeholders, often results in slow and inefficient workflows. Users frequently engage in multiple back-and-forth email exchanges to clarify requirements, finalize imaging parameters, and negotiate pricing. For time-sensitive projects, such delays can lead to missed opportunities and compromised outcomes.
Limited flexibility and data accessibility
Another major challenge lies in the rigid service offerings of individual satellite providers. Due to the lack of integrated data networks from multiple sources, users often have to purchase more imagery than necessary to meet the strict parameters of a single satellite system. This leads to increased costs and resource waste, ultimately discouraging potential projects particularly for smaller organizations. To fully unlock the power of satellite tasking, the geospatial industry must prioritize flexible service models and user-friendly tools that make the technology more accessible and adaptable.
Lack of transparent and consistent pricing
Satellite imagery pricing remains opaque and inconsistent. Users typically lack negotiation leverage and are often unable to access standardized pricing structures. This ambiguity complicates budgeting, planning, and decision-making processes. Establishing transparent, predictable pricing models would enable users to better define their needs, choose suitable solutions, and encourage healthy market competition and innovation across the industry.
Delayed data delivery undermines real-time applications
In today’s fast-paced world, access to real-time or near-real-time data is a crucial requirement for most geospatial projects. Unfortunately, acquiring fresh satellite imagery can take days or even weeks, rendering the data outdated for critical applications such as disaster response, security monitoring, or crop health assessment. Accelerating data acquisition and delivery timelines would significantly expand the range of real-time use cases for satellite data, ultimately enhancing the overall value and applicability of this powerful technology.

Why is satellite tasking important?
Satellite tasking is becoming increasingly essential across various domains, including environmental monitoring, precision agriculture, disaster response, and urban planning. Instead of relying solely on archived imagery, users can proactively request new satellite acquisitions tailored to their specific needs. The following are key reasons why satellite tasking plays a critical role today:
Real-time updates
When up-to-date imagery is needed such as in the aftermath of a natural disaster, infrastructure changes, or agricultural developments, archived data is often outdated. Satellite tasking enables access to near real-time imagery, providing timely insights for informed decision-making.
Customizable accuracy
Many applications require imagery with specific technical parameters, such as high spatial resolution, off-nadir viewing angles, or acquisitions at particular times of day (e.g., morning or afternoon). Satellite tasking allows users to define these specifications, which are rarely fully met by archived datasets.
Enhanced data accessibility
Archived imagery is not always available for the precise location and time required. This is especially true for remote, underserved, or low-priority regions. In such cases, satellite tasking may be the only viable solution to obtain relevant and timely imagery.
Time-series collection
For continuous monitoring projects such as flood tracking, forest change detection, or crop growth analysis users often need imagery collected at regular intervals. Satellite tasking supports the development of time-series acquisition plans, enabling consistent data collection over specific areas during desired timeframes.
Data quality control
Through satellite tasking, users can request imagery free from clouds, shadows, or other quality-degrading factors. This level of control is crucial for applications requiring high-precision analysis, ensuring consistency and minimizing errors caused by poor-quality imagery.
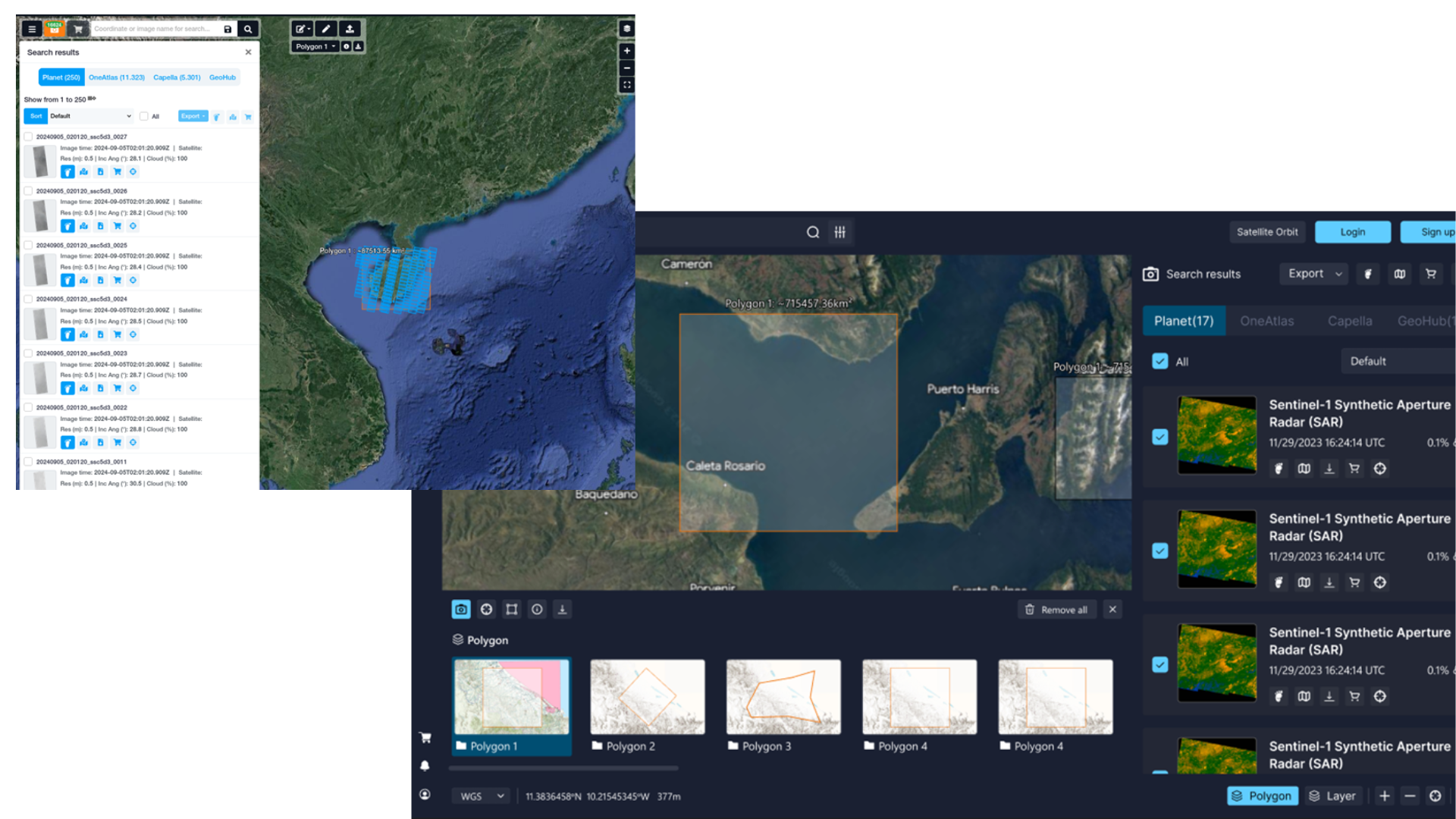
How can users perform satellite tasking on GEOHUB?
Define your area of interest (AOI)
After registering or logging in, the first step is to precisely define the geographic area for image acquisition:
-
Web Interface: Draw the target area directly on the interactive map within the GEOHUB platform. GEOHUB supports urgent tasking, standard tasking, and accessing available archived imagery.
-
AOI Upload: Upload your Area of Interest as a KML, GeoJSON, or Shapefile.
Configure image acquisition parameters
Once the AOI is defined, users can configure the image acquisition parameters:
-
Satellite: Choose a specific satellite or allow GEOHUB to recommend the most suitable option.
-
Spatial Resolution: Select the required spatial resolution (e.g., 30cm, 50cm, 75cm, 1m, 2m, etc.).
-
Timeline: Set the desired time window during which the image should be captured.
-
Cloud Cover Threshold: Specify the maximum acceptable cloud cover percentage (commonly 15–20% or lower).
-
Off-Nadir Angle: Define the acceptable viewing angle, which can affect image clarity and geometric accuracy.
-
Spectral Bands: Indicate the spectral bands required (e.g., RGB, NIR, SWIR, etc.).
-
Priority Level: Choose between standard or high-priority tasking (this affects both cost and delivery time).
Feasibility and pricing review
After receiving the tasking request, the GEOHUB operations team will:
-
Assess the feasibility of tasking based on satellite availability and environmental conditions.
-
Provide a detailed quotation based on your specified parameters.
-
Offer technical consultation and recommend alternative solutions if your original request presents challenges.
Order confirmation and tracking
Once the quotation is approved:
-
Your satellite tasking request will be queued for acquisition.
-
You will receive real-time updates and can track the order status directly within the GEOHUB platform.
-
You will be notified once the imagery is ready.
Receive and utilize your imagery
Upon successful tasking:
-
Your imagery will undergo quality control and preprocessing.
-
Data will be delivered through GEOHUB in your preferred format.
-
Additional processing options are available (e.g., orthorectification, analysis-ready data).
-
Cloud storage and API access are available for enterprise users.
The era of time-consuming email exchanges for satellite tasking is over. GEOHUB delivers a fully integrated and streamlined tasking solution that simplifies the entire process. Users can effortlessly submit acquisition requests, receive instant quotations, and seamlessly integrate the delivered data into their workflows – all within a single platform. This reduction in technical complexity enables users to focus more on their core objectives and less on operational overhead.
If you’re interested in satellite tasking on our GEOHUB platform, please leave your information in the consultation form. Our geospatial experts will get in touch and support you promptly!
